1.概要
複数のスレッドで共有リソースにアクセスするとき、同時に1つのスレッドだけが共有リソースにアクセスできるようにするために、ミューテックス (英: mutex)が使用されます。
2.ミューテックスを使った排他制御
下記のサンプルでは、2 つのスレッドを作成し、実行するスレッド関数としてthread_functionを渡します。thread_function内では、最初に pthread_mutex_lockを使用してミューテックスをロックし、一度に 1 つのスレッドだけが共有リソースにアクセスできるようにします。共有リソースにアクセスした後、pthread_mutex_unlockを使用してミューテックスのロックを解除します。メインでは、pthread_joinを使用して両方のスレッドが終了するのを待ち、最後に pthread_mutex_destroy を使用してミューテックスを破棄します。
ミューテックスを正しく使用しないと、デッドロックが発生する可能性があります。デッドロックは、2 つ以上のスレッドがブロックされ、互いがミューテックスを解放するのを待っているときに発生します。デッドロックを回避するには、複数のミューテックスにアクセスするときは常に同じロック順序を使用します。
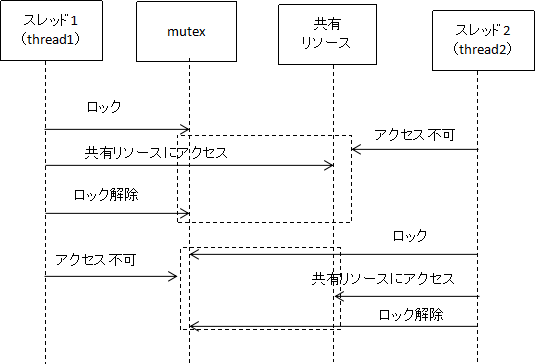
3.サンプル
thread_mutex1.c
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
void* thread_function(void* arg) {
// 共有リソースにアクセスする前にロックする
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
// 共有リソースにアクセス
printf("Thread %ld is accessing the shared resource.\n", pthread_self());
// ロックを解除する
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
return NULL;
}
int main() {
pthread_t thread1, thread2;
// Initialize the mutex
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
// Create two threads
pthread_create(&thread1, NULL, thread_function, NULL);
pthread_create(&thread2, NULL, thread_function, NULL);
// Wait for the threads to finish
pthread_join(thread1, NULL);
pthread_join(thread2, NULL);
// Destroy the mutex
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
return 0;
}
(※1)pthread_create()
新しいスレッドを生成する
(書式)
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_create(pthread_t * thread,
pthread_attr_t * attr,
void * (*start_routine)(void *),void * arg);
引数:
thread:スレッド管理用
attr:スレッド属性、NULLのときはデフォルト
(*start_routine)(void *):スレッドから呼び出される関数へのポインタ
arg:start_routine()の引数で渡すデータのポインタ
戻り値:
成功すると新しく作成したスレッドの識別子が引数threadの指す領域へ格納され、0 が返る。エラーの場合、非 0 のエラーコードが返る。
(※2)pthread_join()
別のスレッドの終了を待つ
(書式)
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_join(pthread_t th, void **thread_return);
引数:
th:待機するスレッドの指定
**thread_return:スレッドの戻り値を格納する領域
戻り値:
成功すると、thの返り値がthread_returnで指し示された領域に格納され、0が返る。エラーの場合、非 0 のエラーコードが返る。
(※3)pthread_self()
呼び出したスレッドのIDを取得する
(書式)
#include <pthread.h>
pthread_t pthread_self(void);
コンパイルするとき、マルチスレッドをサポートするために、pthreads ライブラリーを使用するようにコンパイラーに指示します。
$ gcc -pthread thread_mutex1.c
実行結果

end